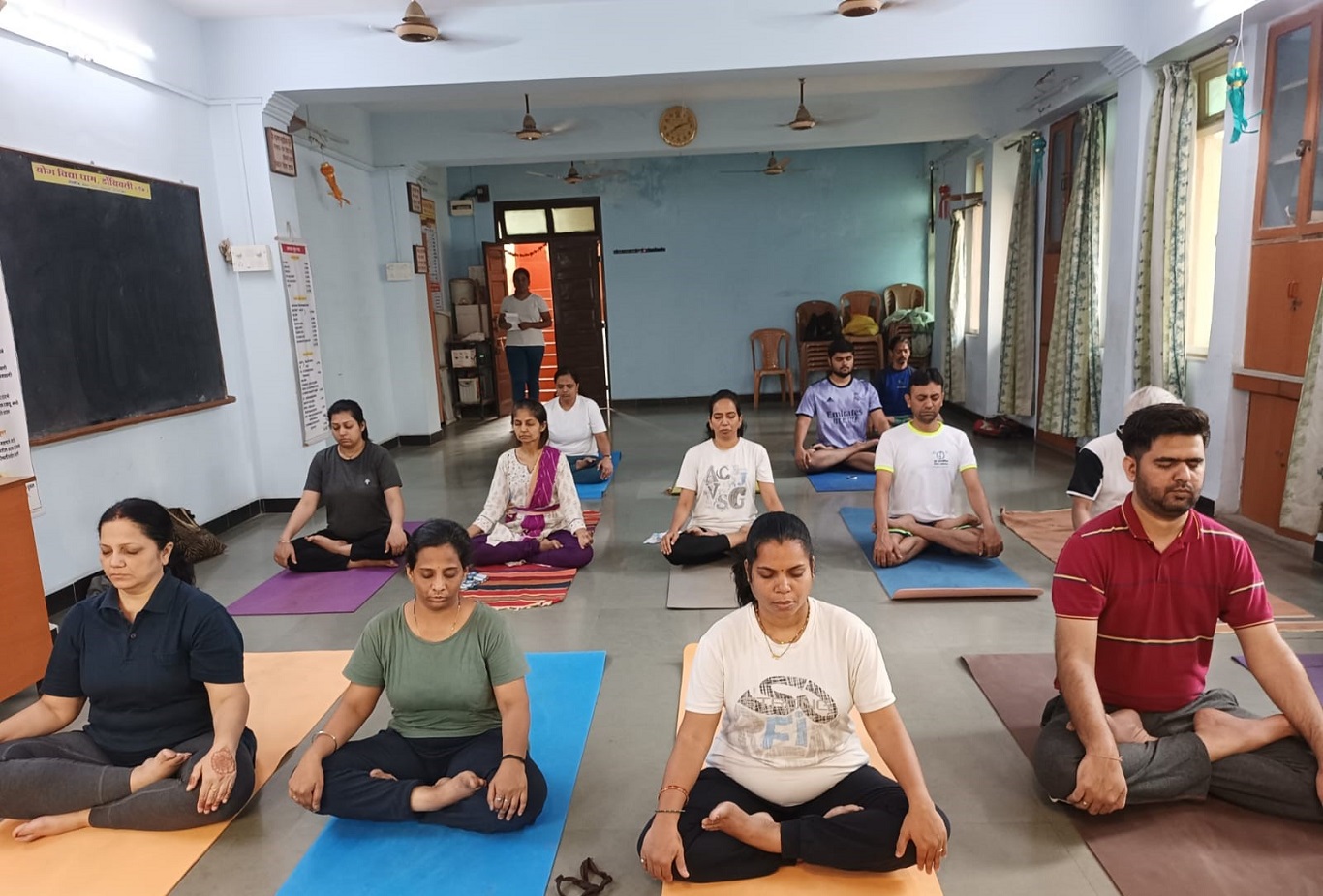
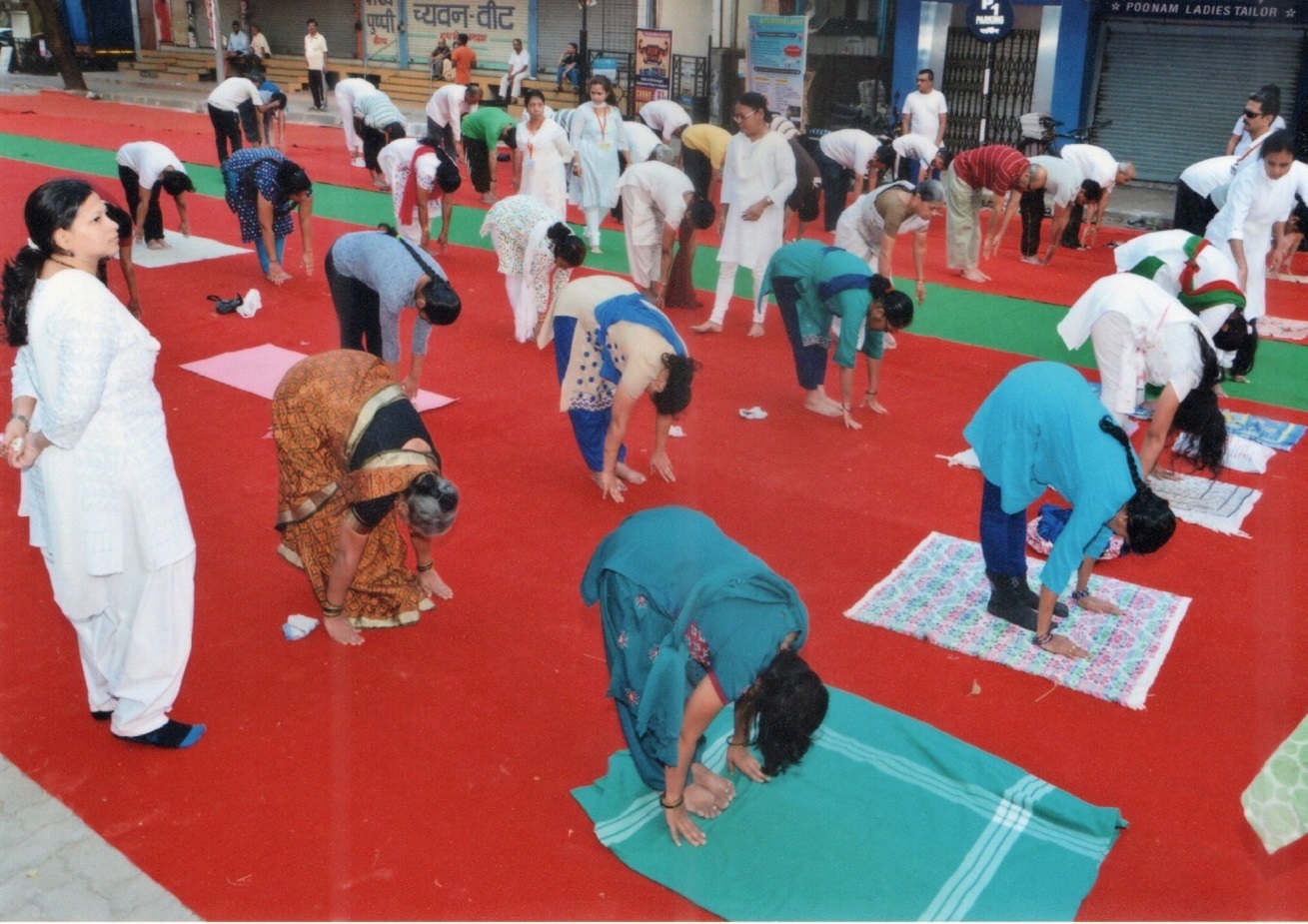
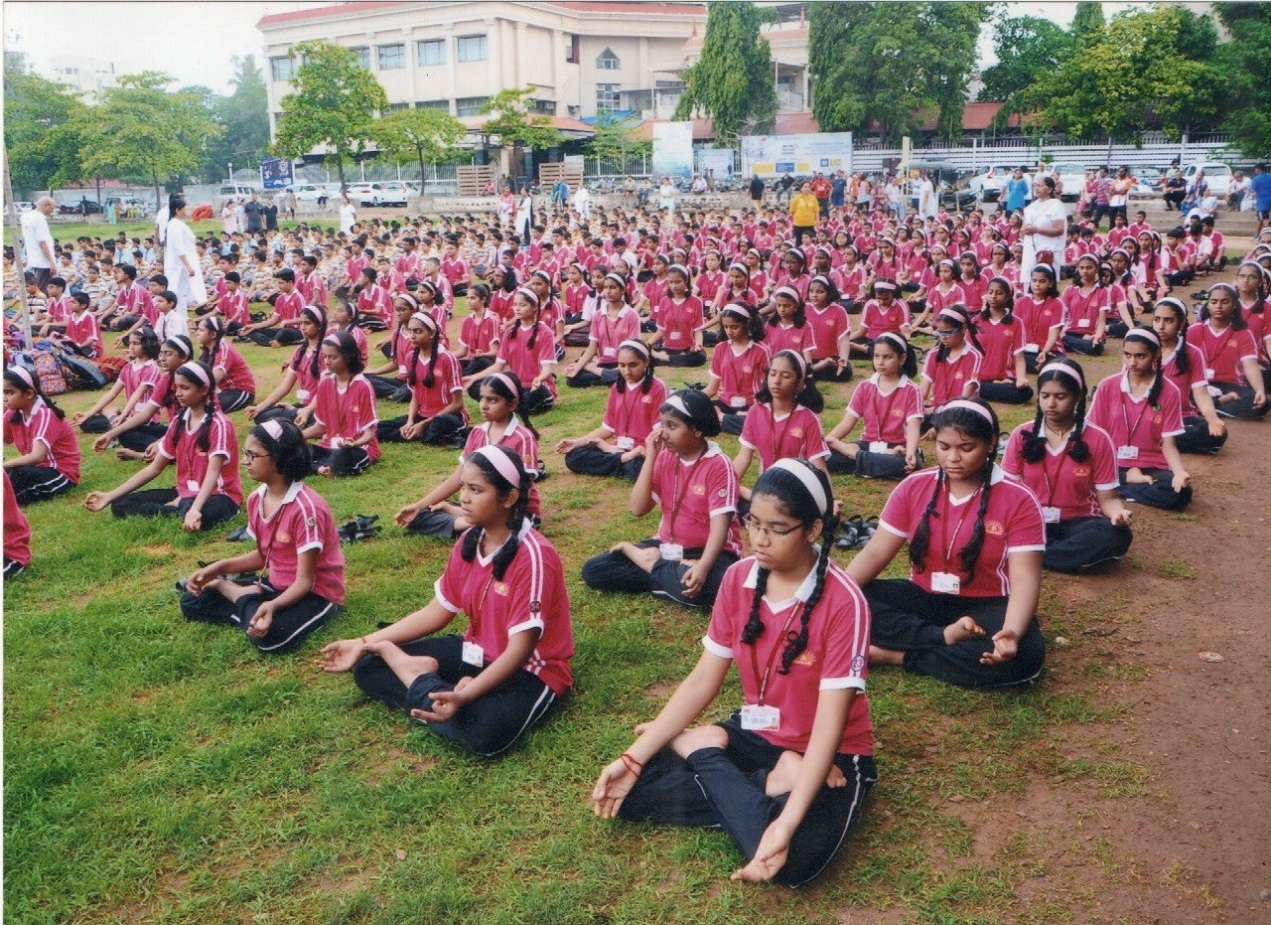
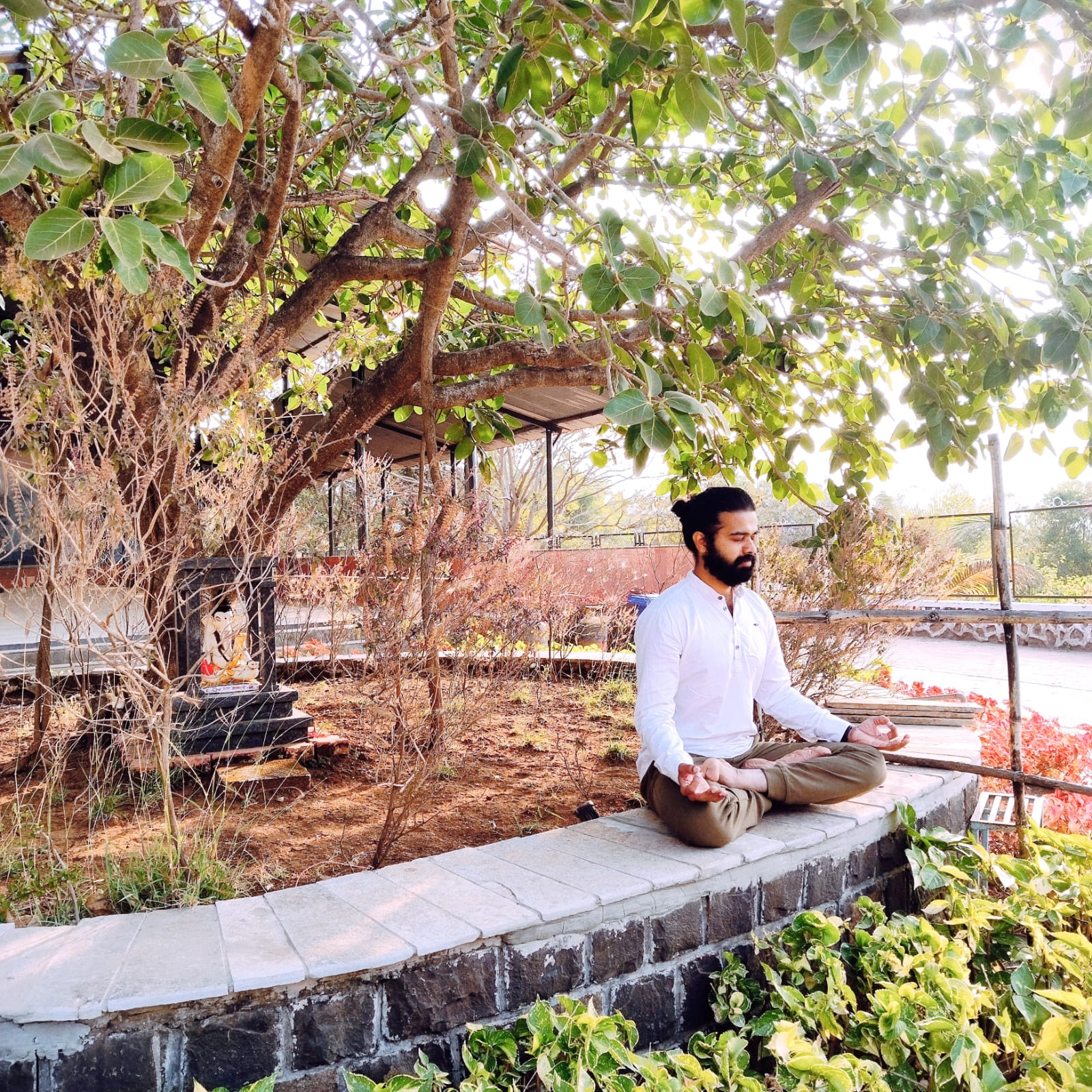
Meditation is an integral part of yoga practice, often seen as the culmination of the physical and breath-centered aspects of yoga. It involves focusing the mind and cultivating a state of mental clarity, calmness, and presence. Here’s how meditation is incorporated into yoga:
1. Preparation:
Before beginning meditation, it’s common to prepare the body and mind through asana (yoga postures) and pranayama (breathing exercises). This helps release physical tension and makes it easier to sit comfortably for meditation.
2. Posture:
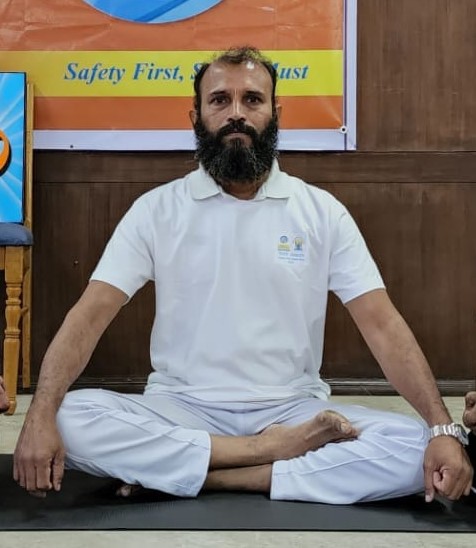
A comfortable and upright posture is essential for meditation. Traditionally, this involves sitting cross-legged on the floor with a straight spine, but you can also use a chair or cushion for support. The key is to find a position that allows you to sit with alertness and ease.
3. Focus:
In meditation, you choose an object of focus. This could be your breath, a specific mantra (a word or phrase repeated mentally), a visualized image, or simply observing your thoughts and sensations as they arise. The object of focus helps anchor your attention.
4. Breath Awareness:
Many meditation practices in yoga involve mindfulness of the breath. You observe the natural rhythm of your breath, paying attention to the inhalation and exhalation. When the mind wanders, gently bring your focus back to the breath.
5. Mantra Meditation:
Some yogic meditation practices involve repeating a specific mantra silently or audibly. Mantras are sacred sounds or words that are believed to have a transformative effect on the mind and consciousness.
6. Chakra or Energy Center Meditation:
In certain forms of yoga, practitioners focus on specific energy centers or chakras within the body. This can involve visualization and concentration on these energy points to balance and align them.
7. Body Scan:
Body scan meditation involves systematically bringing awareness to different parts of the body, often starting from the toes and moving up to the head. This practice helps you connect with physical sensations and release tension.
8. Guided Meditation:
Guided meditation sessions are led by a teacher or recorded audio. They provide verbal instructions and visualization to guide your meditation experience. This can be particularly helpful for beginners.
9. Silent Meditation:
In silent meditation, you sit quietly without external guidance, focusing on your chosen object of meditation or simply observing the flow of your thoughts and emotions.
10. Meditation Duration:
The duration of meditation can vary from a few minutes to an hour or more, depending on your preference and experience. It’s important to start with a manageable duration and gradually extend it as you become more comfortable with the practice.
11. Integration:
The benefits of meditation often extend beyond the meditation session itself. Practitioners aim to carry the sense of presence, calmness, and awareness cultivated during meditation into their daily lives.
Meditation in yoga serves as a tool for developing inner peace, self-awareness, and a deeper understanding of the mind. It can help reduce stress, improve concentration, and promote emotional balance. As with any aspect of yoga, consistency and patience are key to experiencing the full benefits of meditation.